Introduction to Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind
Yuval Noah Harari’s Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind offers a profound exploration of the human journey from ancient times to the modern era. This Sapiens summary delves into the major revolutions that have shaped humanity, including the Cognitive, Agricultural, and Scientific Revolutions. Harari masterfully weaves science, history, and anthropology to explain how Homo sapiens rose to dominate the planet.
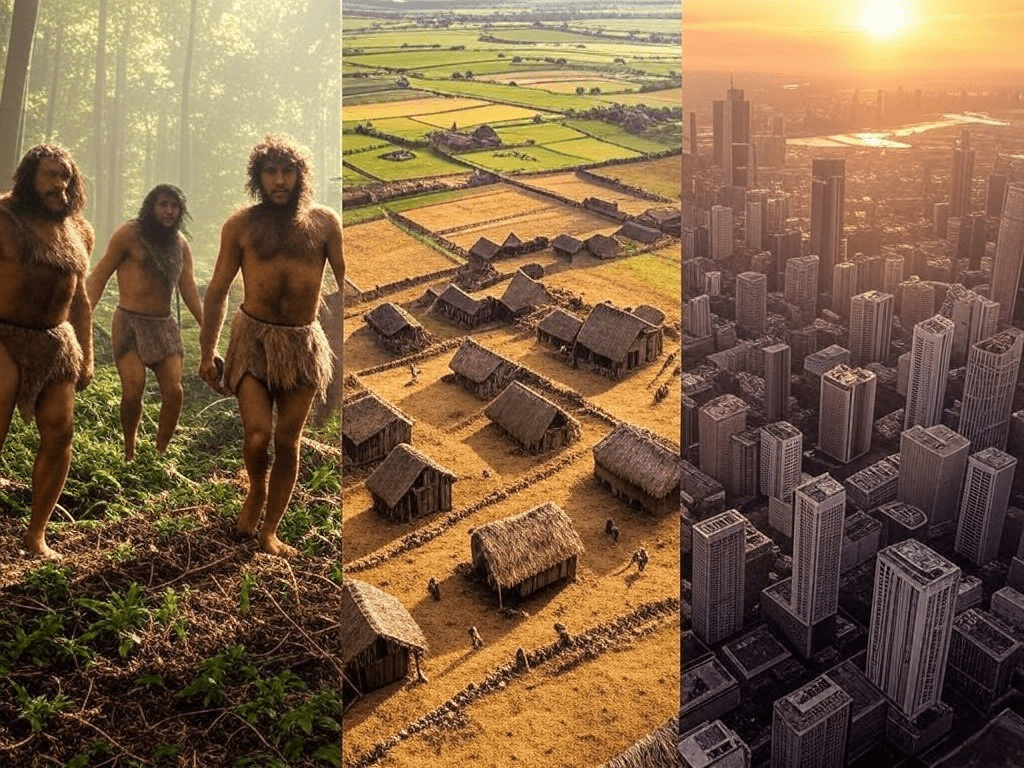

The Cognitive Revolution: Birth of Human Imagination
Approximately 70,000 years ago, the Cognitive Revolution marked a pivotal moment in human history. This era introduced complex language and abstract thinking, enabling early humans to cooperate in large groups. The ability to create shared myths, beliefs, and social structures allowed Homo sapiens to outcompete other human species. In this Sapiens summary, Harari emphasizes how these cognitive advancements were the foundation of societal development.
Storytelling became a critical tool for unity and survival. Shared beliefs in gods, nations, and money fostered trust and large-scale cooperation. This shift set the stage for more complex societies and technological innovation, illustrating the power of imagination in shaping our world.
The Agricultural Revolution: Cultivating Civilizations
The Agricultural Revolution, around 12,000 years ago, drastically altered human lifestyles. Transitioning from foraging to farming led to permanent settlements and population growth. However, this shift brought both progress and challenges. In this Sapiens book summary, Harari argues that while agriculture supported larger communities, it also introduced social hierarchies, diseases, and environmental strain.
Farming required more labor and led to inequalities as land ownership became a symbol of power. Domestication of plants and animals transformed ecosystems and paved the way for organized societies, governments, and economies. The Agricultural Revolution was a double-edged sword—promoting advancement but also societal division.
The Unification of Humankind: Connecting the World
As civilizations expanded, humanity began forming interconnected societies through trade, empires, and religion. Harari explores how money, empires, and universal religions unified diverse cultures. This global connection allowed ideas, goods, and technologies to spread, fueling progress and conflict alike. This Sapiens synopsis reveals how globalization has deep roots in history.
Money became a universal medium of exchange, empires imposed order, and religions provided shared moral codes. These systems enabled unprecedented cooperation across cultures, accelerating human development. The interconnectedness we experience today stems from these historical integrations.
The Scientific Revolution: Power Through Knowledge
The Scientific Revolution, beginning around 500 years ago, fundamentally changed how humans perceive and interact with the world. Harari highlights how the pursuit of knowledge led to technological innovations, industrial growth, and modern capitalism. In this Sapiens summary, the emphasis is on how science and imperialism went hand-in-hand, driving expansion and discovery.
Scientific progress spurred economic growth and global exploration, reshaping societies. The quest for knowledge fostered advancements in medicine, industry, and technology—but also environmental degradation. Harari questions whether this progress has truly led to human happiness or merely fueled endless growth.
Conclusion: Reflecting on Humanity’s Path
Yuval Noah Harari’s Sapiens challenges readers to reflect on humanity’s past and future. From the Cognitive Revolution to modern capitalism, Harari illustrates how human cooperation, myths, and scientific ambition have shaped our societies. This sapiens summary encourages us to consider how these developments influence our present lives and future trajectory.
Understanding our history allows us to question the systems that govern us and imagine better paths forward. Harari leaves readers contemplating the cost of progress and the future of Homo sapiens in an ever-changing world.
What are your thoughts on humanity’s evolution and the challenges ahead? Share your insights in the comments below! If you enjoyed this Sapiens summary, explore more thought-provoking book reviews on our blog.
You might be interested in reading The War of the Worlds by H. G. Wells as well.